What is a stack overflow?
From Wikipedia:
In software, a stack overflow occurs when too much memory is used on the call stack. In many programming languages, the call stack contains a limited amount of memory, usually determined at the start of the program.
The stack is a data structure that keeps record of the point the subroutines of a program should return control to when they finish executing. The return addresses are pushed in the stack as the subroutines are being invoked, when the subroutine finish its execution the return address is pulled from the stack. If there are many subroutines and there is no space in the stack a stack overflow happens.
Also in the stack is intended to store local variables so if a local variable is too large is more probable the stack doesn't have space to store it, if this is the case a stack overflow happens too.
Wikipedia includes a nice diagram picturing the stack when a DrawLine subroutine is called from another subroutine called DrawSquare, I hope this picture helps to understand better the stack structure.
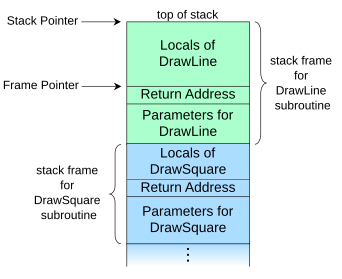
There are two main causes of a stack overflow: deep function recursions and excessively large stack variables. Since these are common terms in almost all programming languages a stack overflow can happen besides the complexity of the language.
Guffa contribution: The stack doesn't have anything to do with garbage collection. Modern applications have a larger stack, which makes it slightly less likely to get a stack overflow, but other than that there is no difference.
A stack overflow happens when you use too much stack space. There is generally two situations when this happens:
The first is when you have an error in the code, causing a recursive loop without an exit. For example a property reading from itself:
public int Length {
get {
return Length;
}
}
The second is when you have a recursive loop that is too deep. As the stack space is limited, you can only nest an algorithm a certain number of times. If your algorithm is nested too deep so that it runs out of stack space before it exists, you get a stack overflow. Example:
public bool Odd(int value) {
if (value == 0) {
return false;
} else {
return !Odd(value - 1);
}
}
If you call this method with a too large value, it will nest too deep and cause a stack overflow.
The stack contains a number of stack frames and is stored in memory. Every time a function is called, a new stack frame is added to the stack. A stack frame contains the arguments to be passed to the function being called, and the return address, so that when the called function has finished the cpu knows where to return to so it can continue executing the calling function. The stack frame may also contain memory to be used by local variables of the function being called.
In this example, the Main function called WriteCustomerDetails and that called PrintToConsole to write out individual bits of data that the WriteCustomerDetails function looked up:
'=======top of stack====================='
Function: PrintToConsole
Arg: John Smith, 34 Acacia Avenue, Age 23
'-----------------------------------------------------------'
Function: WriteCustomerDetails
Arg: John Smith
'-----------------------------------------------------------'
Function: Main
'======bottom of stack==================='
A stack overflow occurs if enough space for the stack was not reserved. Usually a stack sits in one large contiguous block of memory, so isn't divided into chunks, this means one big piece of memory is needed for it, and this makes it hard for the runtime to try and grow the space reserved for the stack if it fills up.
A stack-overflow can often occur when a function is accidentally written that calls itself. Sometimes it's ok for a function to call itself as long as there is an 'if' or some condition in the function that stops the calls at some point. This is called a recursive function. But, if there is no stopping and the function keeps calling itself, or maybe two or more functions keep calling each other, then very quickly they will eat all of the stack memory up. When there's none left, you get a stack-overflow and the program crashes.
It is possible for this to happen in any program, they don't necessarily have to be complex, and it can happen in code running a website. And, it can occur in scripting languages too.